Test your current internet speed
Before you get started, test your current internet speed. Use your speed test result as a baseline and compare the results as you go through your journey on reaching a faster internet connection.
SpeedtestThe term “broadcast domain” holds a crucial position. It is a fundamental concept that plays a vital role in the transmission of data packets across a network.
This article will delve into the depths of broadcast domains, explaining what they are, their importance in network architecture, and how they impact data communication. So, let’s dive in and unravel the mysteries of the broadcast domain.
1. What is a Broadcast Domain?
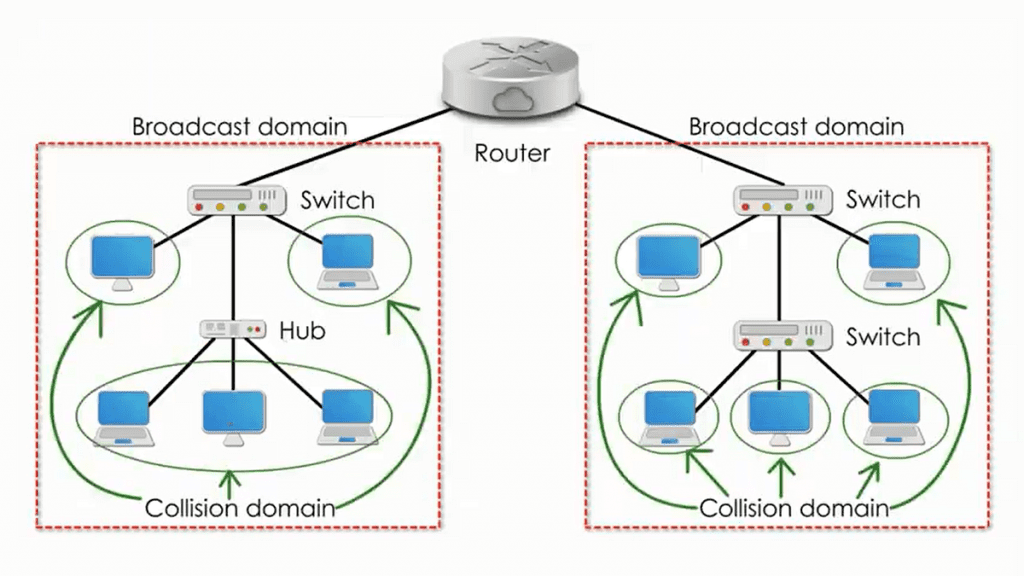
A broadcast domain refers to a logical division of a computer network in which all devices can directly send broadcast messages to each other. In simpler terms, it represents a group of interconnected devices that receive and process broadcast packets. Broadcast messages are data packets sent to all devices within a network, typically used for address resolution, network discovery, and other essential network operations.
2. How Does a Broadcast Domain Work?
Within a broadcast domain, when a device sends a broadcast message, it is received by all other devices in the same domain. Each device evaluates the message and determines whether it is relevant or not based on its network address. Devices that recognize the message’s relevance process it further, while others discard it. This mechanism ensures efficient communication within the domain, as only devices that require the information act upon it.
3. Limiting Broadcast Domain Size
As networks grow in size and complexity, it becomes essential to limit the size of broadcast domains to maintain network performance and reduce unnecessary traffic. Two common approaches used to achieve this are VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) and Layer 3 routing.
3.1 VLANs: Segmenting Broadcast Domains
VLANs allow network administrators to logically segment a network into smaller, isolated broadcast domains. Devices within a VLAN communicate with each other directly, reducing the scope of broadcast messages. VLANs provide flexibility, security, and better management of network resources, enabling efficient data transmission.
3.2 Layer 3 Routing: Interconnecting Broadcast Domains
Layer 3 routing involves the use of routers to interconnect different broadcast domains. By routing traffic between domains, routers restrict the reach of broadcast messages to a specific domain, preventing them from flooding the entire network. This segmentation helps in containing broadcast traffic and enhancing network performance.
4. Benefits of Controlling Broadcast Domains
Controlling broadcast domains offers several advantages, including:
- Improved Performance: By limiting the scope of broadcast messages, network congestion is reduced, resulting in improved overall network performance.
- Enhanced Security: Smaller broadcast domains minimize the potential impact of malicious broadcast-based attacks, enhancing network security.
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Broadcast domains allow better utilization of network resources, ensuring efficient data transmission and reducing unnecessary network traffic.
- Ease of Troubleshooting: Smaller broadcast domains facilitate localized troubleshooting, making it easier to identify and resolve network issues.
5. Broadcast Storms: Causes and Mitigation Strategies
A broadcast storm occurs when a network is overwhelmed with continuous broadcast messages, resulting in severe network degradation or even a complete network outage. Broadcast storms can be caused by misconfigured devices, network loops, or even malicious activities.
To mitigate broadcast storms, network administrators employ strategies such as:
- Implementing Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to prevent network loops.
- Monitoring network traffic and using broadcast storm control mechanisms.
- Utilizing VLANs to segment the network and isolate broadcast domains.
- Employing rate-limiting techniques to control the number of broadcast messages.
6. Broadcast Domains and Network Performance
The size of a broadcast domain significantly impacts network performance. Large broadcast domains increase the likelihood of network congestion, collisions, and inefficient resource utilization.
On the other hand, smaller broadcast domains improve network performance by reducing unnecessary traffic and enhancing data transmission efficiency.
7. Security Implications of Broadcast Domains
Broadcast domains play a crucial role in network security. By limiting the scope of broadcast messages, potential attackers have a harder time infiltrating the network through broadcast-based attacks.
Smaller broadcast domains enable better network segmentation and access control, minimizing the impact of security breaches.
8. Broadcast Domains in Virtualized Environments
In virtualized environments, broadcast domains are essential for efficient communication between virtual machines (VMs) and the underlying physical network.
Technologies like virtual switches and virtual LANs enable administrators to create and manage virtual broadcast domains, ensuring optimized network performance within virtualized infrastructures.
9. The Role of Broadcast Domains in Internet of Things (IoT) Networks
In the realm of Internet of Things (IoT), where numerous devices connect and interact, broadcast domains become critical for efficient communication and resource management.
By segregating devices into smaller broadcast domains, IoT networks can minimize unnecessary traffic, optimize data transmission, and enhance security.
10. Best Practices for Designing Broadcast Domains
When designing broadcast domains, it is essential to consider the following best practices:
- Analyze Network Traffic: Understand the traffic patterns and requirements of the network to determine the optimal size and number of broadcast domains.
- Segment Networks: Use VLANs or Layer 3 routing to segment networks and create smaller broadcast domains based on logical groupings.
- Implement Access Control: Apply appropriate access control mechanisms to restrict communication between broadcast domains and enhance network security.
- Regularly Monitor and Update: Continuously monitor the network, identify potential issues, and update the design of broadcast domains to adapt to changing network requirements.
11. Troubleshooting Broadcast Domain Issues
When troubleshooting broadcast domain issues, consider the following steps:
- Check for misconfigured devices or network loops.
- Verify VLAN configurations and ensure proper VLAN tagging.
- Monitor network traffic for abnormal broadcast behavior.
- Utilize diagnostic tools to identify the source of broadcast storms or excessive broadcast traffic.
- Collaborate with network administrators or professionals to resolve complex broadcast domain issues.
12. The Future of Broadcast Domains
As networks evolve and new technologies emerge, the concept of broadcast domains will continue to play a crucial role.
With the rise of virtualization, cloud computing, and IoT, efficient management of broadcast domains will become increasingly important for ensuring optimal network performance, security, and scalability.
Conclusion
Broadcast domains are the building blocks of efficient data transmission in computer networks.
By understanding the concept, benefits, and strategies associated with broadcast domains, network administrators can optimize network performance, enhance security, and facilitate the seamless flow of information across interconnected devices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the primary purpose of a broadcast domain?
The primary purpose of a broadcast domain is to facilitate communication between devices within a specific network segment, enabling the efficient transmission of broadcast messages. - Can two devices in different broadcast domains communicate directly?
No, devices in different broadcast domains cannot communicate directly via broadcast messages. Communication between devices in different domains requires the use of routing or other interconnection mechanisms. - How can VLANs help in controlling broadcast domains?
VLANs allow network administrators to segment a network into smaller broadcast domains, isolating traffic within each VLAN and preventing unnecessary broadcast messages from flooding the entire network. - What are some common signs of a broadcast storm?
Common signs of a broadcast storm include network slowdowns, excessive network traffic, high CPU utilization on network devices, and unresponsive network services. - How does the size of a broadcast domain affect network performance?
Larger broadcast domains can lead to network congestion, collisions, and inefficient resource utilization, negatively impacting network performance. Smaller broadcast domains enhance performance by reducing unnecessary traffic and optimizing data transmission efficiency.

The visionary founder behind SpeedtestGo, an innovative platform dedicated to helping users measure and optimize their internet speed. With a deep-rooted love for technology and a mission to empower individuals with reliable internet connections, Shawn has created a remarkable space where users can test their internet speed and gain valuable insights and information through engaging blog content.


![Internet Stability Test: Optimize Your Online Experience [2024]](https://speedtestgo.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Internet-Stability-Test-Optimize-Your-Online-Experience-2023-400x250.jpg)




![Why does Funimation keep buffering? [How to fix]](https://speedtestgo.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/apps.21747.13510798887159856.84914116-e545-472a-a1dd-5553f2439ccb-400x250.jpg)
