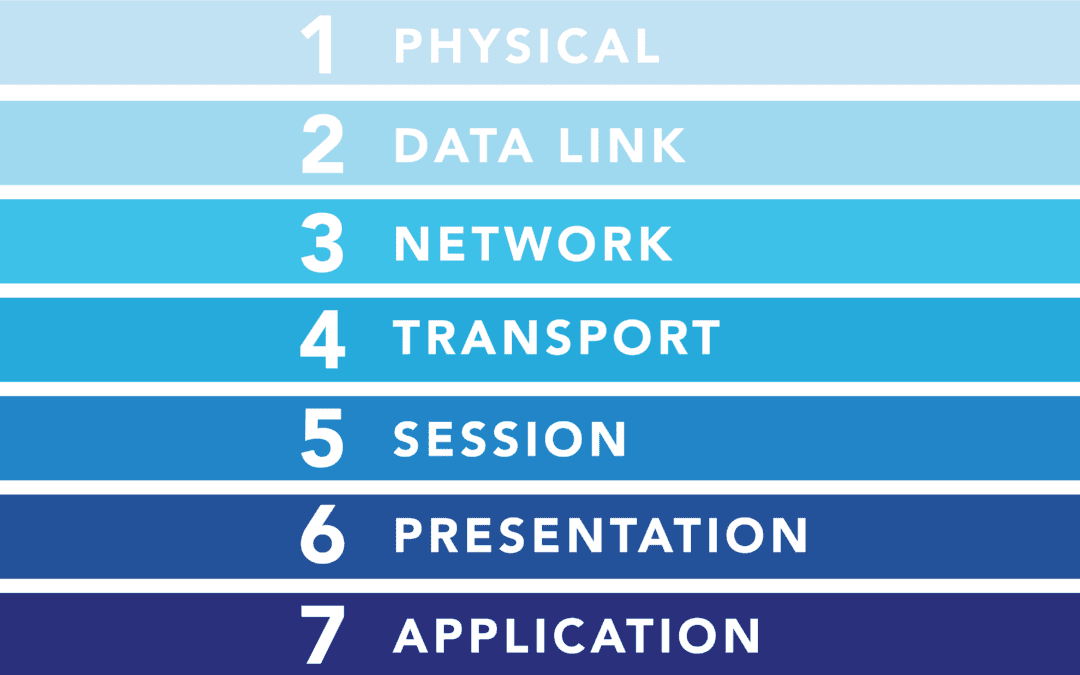
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a conceptual framework that standardizes the functions of a communication system into seven distinct layers.
Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), the OSI model provides a structured approach to network communication, facilitating interoperability between different systems and devices.
In this article, we will delve into each layer of the OSI model, exploring its purpose and significance in the realm of networking.
Layer 1: Physical Layer
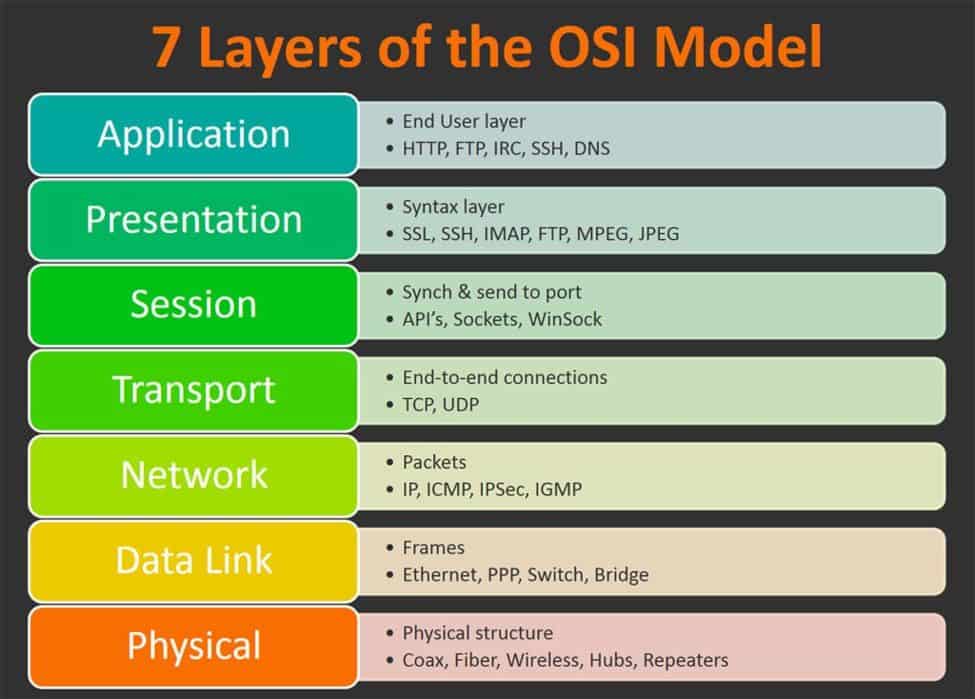
The Physical Layer is the lowest layer of the OSI model and deals with the transmission of raw data over physical media. It encompasses electrical, mechanical, and procedural aspects of communication. This layer defines the physical characteristics of the network, such as cables, connectors, and signaling techniques.
Layer 2: Data Link Layer
The Data Link Layer provides a reliable and error-free connection between two adjacent nodes on a network. It is responsible for the framing and synchronization of data, as well as error detection and correction. Ethernet and Wi-Fi are examples of protocols that operate at this layer.
Layer 3: Network Layer
The Network Layer enables the transfer of data between different networks. It establishes logical paths, known as routes, for data to travel from the source to the destination. IP (Internet Protocol) is a commonly used protocol at this layer, and routers are the primary devices that operate at Layer 3.
Layer 4: Transport Layer
The Transport Layer ensures the reliable delivery of data across a network. It provides end-to-end error recovery, flow control, and segmentation of data. Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) are two prominent protocols at this layer.
Layer 5: Session Layer
The Session Layer manages the communication sessions between applications running on different devices. It establishes, maintains, and terminates connections between applications, allowing them to exchange data. This layer ensures the synchronization and coordination of data exchange.
Layer 6: Presentation Layer
The Presentation Layer is responsible for data representation and transformation. It translates data into a format that can be understood by the receiving application. Encryption and decryption, compression, and formatting are some functions performed at this layer.
Layer 7: Application Layer
The Application Layer is the topmost layer of the OSI model and represents the interface between the user and the network. It includes protocols and services that enable specific applications to access network resources. Examples of protocols at this layer include HTTP, FTP, and SMTP.
Conclusion
The OSI model provides a comprehensive framework for understanding and implementing network communication.
Each layer plays a vital role in ensuring reliable, efficient, and secure data transmission.
By adhering to the principles of the OSI model, network administrators, and engineers can design and troubleshoot complex networks with ease.
FAQs
1. What is the purpose of the OSI model?
The OSI model serves as a conceptual framework for standardizing network communication and promoting interoperability between different systems.
2. How many layers are there in the OSI model?
The OSI model consists of seven layers: Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, and Application.
3. What is the role of the Physical Layer?
The Physical Layer deals with the transmission of raw data over physical media and defines the physical characteristics of the network.
4. Which layer is responsible for error detection and correction?
The Data Link Layer is responsible for error detection and correction, ensuring reliable data transmission.
5. What is the Application Layer?
The Application Layer represents the interface between the user and the network, allowing specific applications to access network resources.