One of the most important factors to take into account when selecting an internet service provider is internet speed. It impacts how many jobs your network can do at once and how quickly you can complete tasks online. Unless you live alone and exclusively use Facebook, you might require more speed than the minimum.
This blog will goes over the importance of good internet speed, the different terms that are used when dealing with internet speed, and the different internet connections/types you can have. We will also be discussing how much internet speed you will need.
What is internet speed and why does it matter?
Internet speed
The amount of time it takes for a specific amount of data to travel from a server to your device and vice versa is known as internet speed.
Whether you’re watching Netflix streaming films, tweeting, or participating in a Zoom meeting, you’re using your smartphone to download and upload data packets. Your internet connection’s capacity, expressed in megabits per second (Mbps), determines how quickly you can move all of this data.
Your internet service provider determines your internet speed on a home Wi-Fi network. The amount you can spend for faster speeds and the provider’s technological capabilities determine what you can get. Naturally, faster connections typically cost more each month.
Why it matters
Because it determines the limitations of what you can do online, internet speed is important. Although most online users would be content with download speeds of 100 Mbps, internet service providers offer plans with speeds ranging from less than 1 Mbps (very sluggish) to 5,000 Mbps (insanely fast).
When your internet connection is fast enough, you can perform high-bandwidth tasks (like downloading a major video game or streaming in 4K) without having to worry about lag time, buffering, or dropped connections.
Fast internet also makes it possible to use numerous Wi-Fi devices simultaneously or multitask through Wi-Fi on the same device. As a result, having a quicker internet connection isn’t only about speed; it’s also about capacity.
Terms you should know to understand the internet better
Learn more about Internet speeds by reading the following definitions:
- Bandwidth: A network connection’s bandwidth measures the total number of frequencies, or capacity, that it can support at any given time. A network can handle more data flow at once if it has higher bandwidth. The number of devices that can connect to the network concurrently will depend on this.
- Download Speed: The speed at which data goes from the internet to your device is known as download speed. A faster download speed allows you to stream, download files, and access websites more quickly.
- Upload Speed: The speed at which data travels from your device to the internet is referred to as upload speed. Uploading files or images to social media or other websites can take less time if you have a faster upload speed.
- Jitter: Jitter occurs when data packets are sent over your network connection with a time delay. Congestion on the network, as well as path improvements, are common causes.
- Ping/Latency: Ping, also known as latency, is a particular metric that has an effect on online gaming and a few other activities. The time it takes for your network to transfer data from your computer to a remote server and back is known as ping.
- Mbps: We measure internet speeds in “megabits per second”. The bandwidth of an internet connection, or the amount of data that can be transferred per second, is represented by this number. Read more to learn how Mbps and MBps differ from one another.
- Wi-Fi: With Wi-Fi, devices may connect wirelessly to the internet, eliminating the need for hardware connections like Ethernet cables.
The different internet connections
Learn about the various internet connection types and which browsing patterns they best suit before choosing an internet service provider.
You’ll discover that some sorts of internet connections are more suited for the activities you prefer based on your online usage.
Cable

Broadband access is a type of cable Internet connection. Users can access the Internet using cable TV lines using a cable modem.
Cable modems can provide exceptionally fast Internet access, making cable a feasible option for many people.
Dial-up
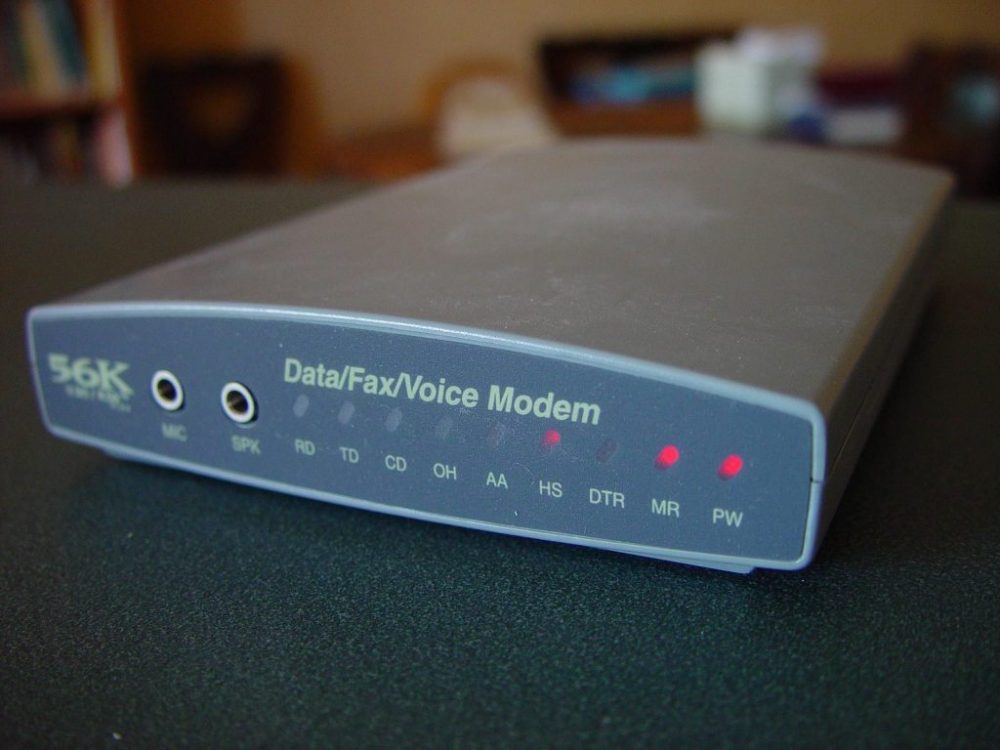

Dial-up internet service is inexpensive, but it is slow. After the computer dials a phone number, an internal or external modem connects to the Internet.
This analog signal is transformed to digital by the modem and routed over a public telephone network-connected landline. The quality of telephone lines varies, and the connection can be spotty at times.
Interference occurs frequently on the lines, affecting the speed, which ranges from 28 to 56 kilometers per hour. A computer or other device that shares the same line as the telephone cannot be used simultaneously.
DSL
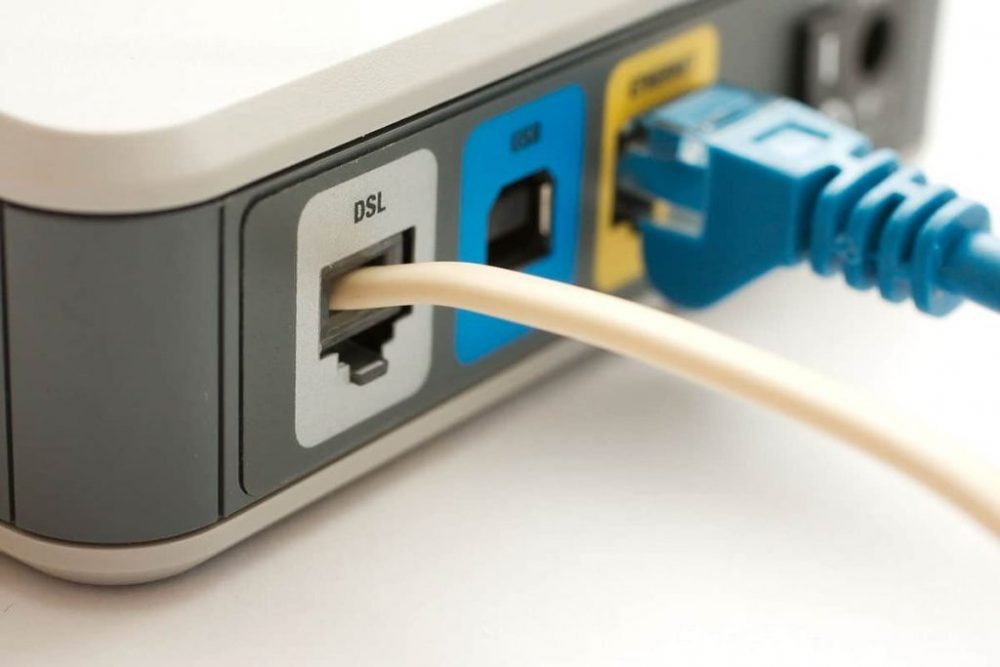

DSL stands for Digital Subscriber Line. It is a connection to the internet that is constantly “on.”
Because two lines are used, your phone will not be tethered when your PC is connected.
To connect, you don’t even need to dial a phone number. DSL employs a router to transfer data, with connection speeds ranging from 128K to 8 Mbps depending on the service.
Fiber-optic
Fiber is one of the best when searching for a fast internet connection to your home or company, providing a quicker and more dependable connection than cable or DSL.
Rather than using electricity to convey data, fiber optic internet employs microscopic strands of glass coated in plastic to transmit data as light.
Recommended for heavy users who want to stream, game, video chat, and download large files at the fastest possible rates. Verizon Fios is the major provider.
Fixed Wireless

Wireless, or Wi-Fi, connects to the internet without the use of telephone lines or wires, as the name implies. Radiofrequency is used instead. Wireless is an always-on connection that may be accessed from almost any location. Wireless network coverage regions are expanding by the minute. The speeds will vary, ranging from 5 Mbps to 20 Mbps.
Satellite
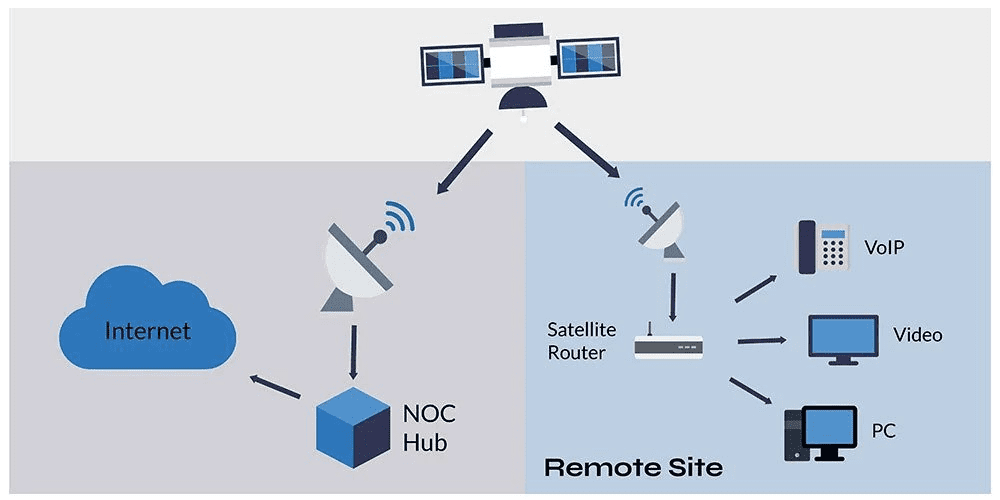
Satellite accesses the internet via a satellite in Earth’s orbit. When compared to cable and DSL, the enormous distance that a signal travels from earth to satellite and back results in a delayed connection. The speed of a satellite connection ranges from 512K to 2.0 Mbps.
How much internet speed do you need?
So now that we know what the different internet connections are and how they work, how do we decide what is best for our home or office?
You and your family may benefit from a specific type of internet connection depending on your browsing habits.
Keep in mind that some types of internet connections may or may not be available where you reside and that companies offering the same type of connection may offer wildly different speeds.
If you’re looking for the best internet connection for your house, weigh the pros and cons of DSL vs. cable, cable vs. fiber internet, and more.